-11 %
Wheel aligner geoliner® 630 Hofmann
- SKU: BD70455
13,999.00 €
15,730.00 €
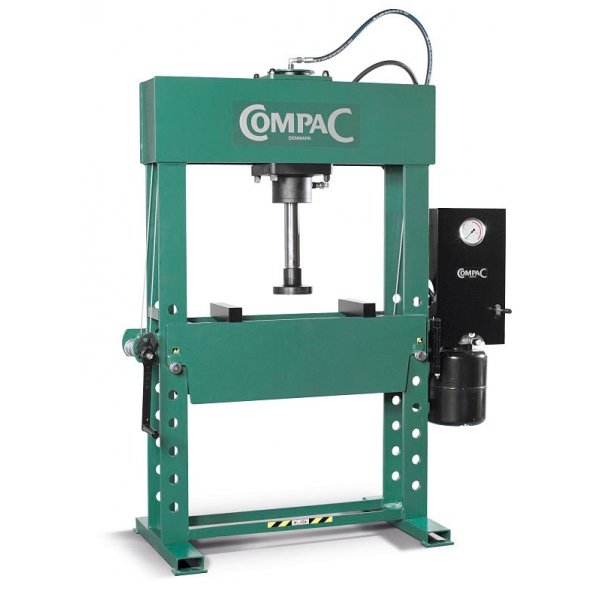
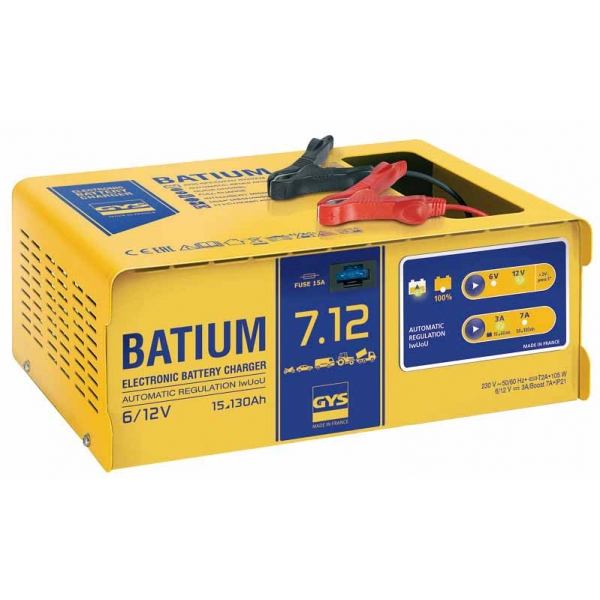
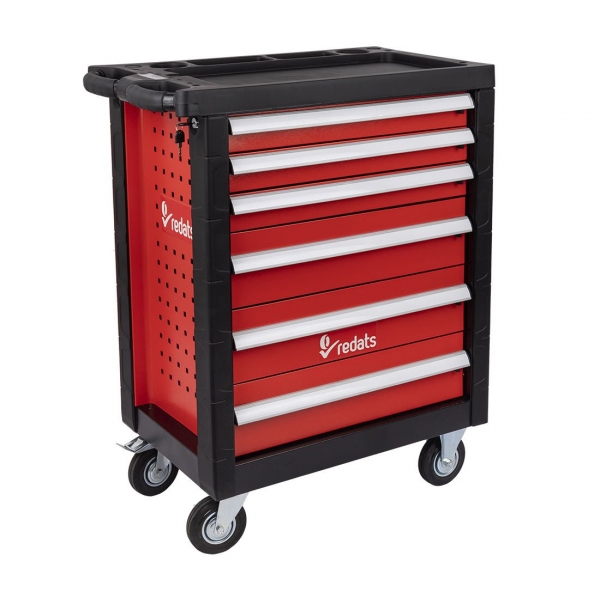
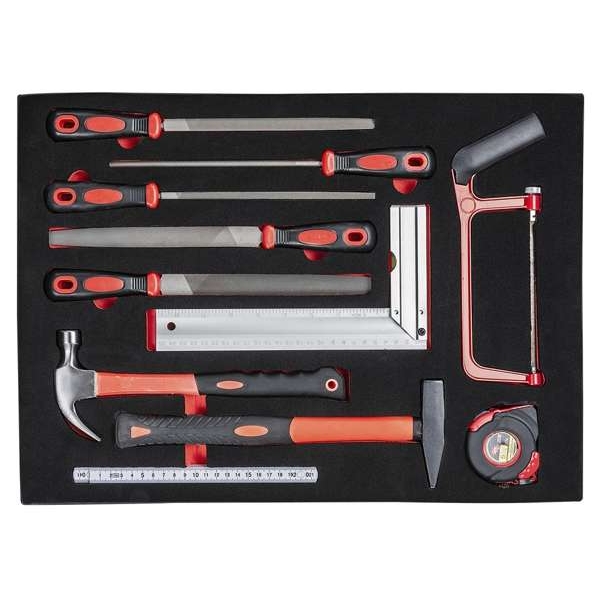

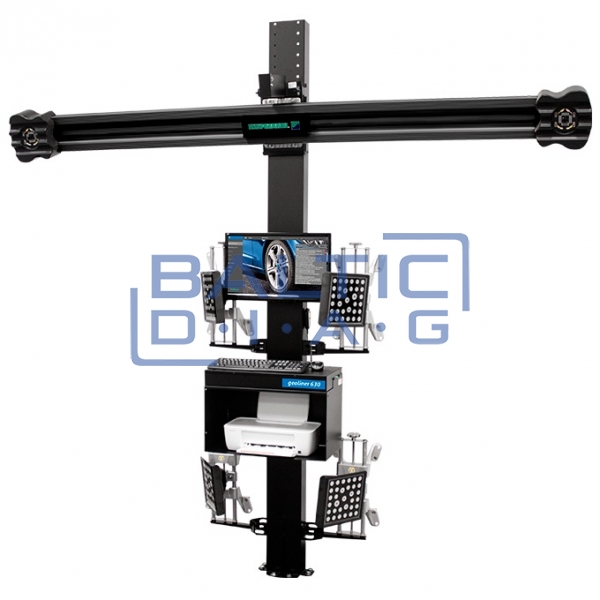





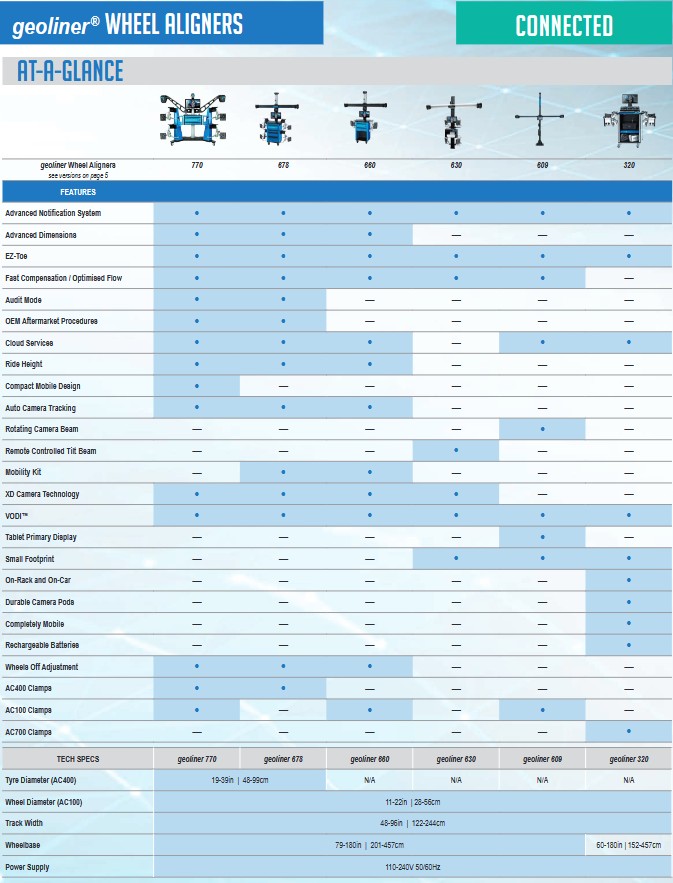












,%2012-kampės-600x600.jpg)